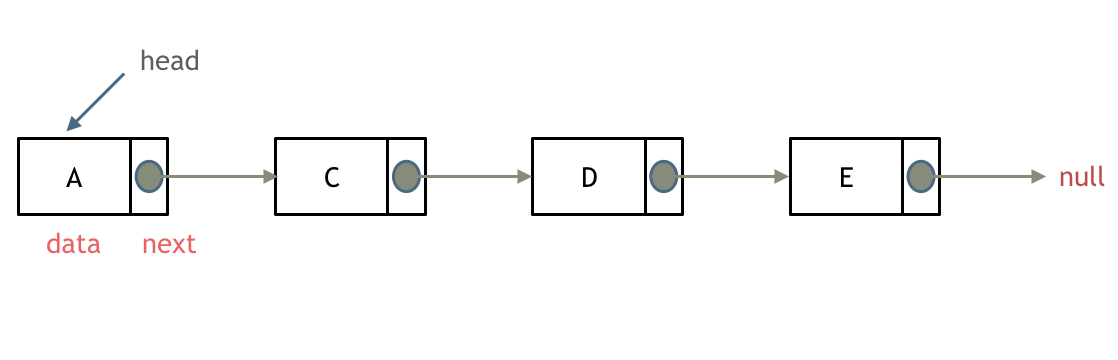
单链表: 指针域只能指向节点的下一个节点。
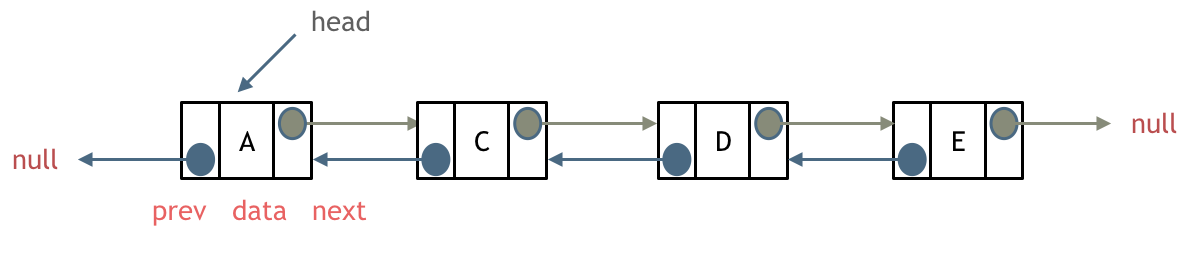
双链表: 每一个节点有两个指针域,一个指向下一个节点,一个指向上一个节点。双链表 既可以向前查询也可以向后查询。
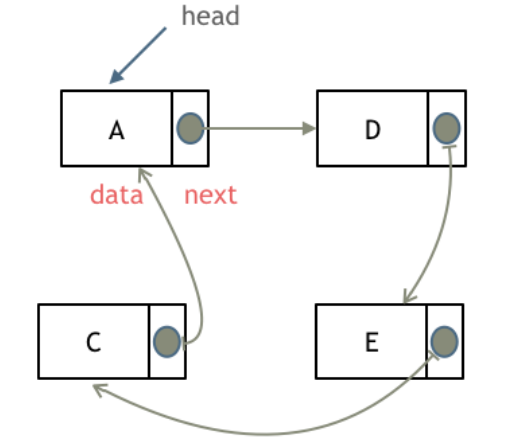
循环链表: 就是链表首尾相连。循环链表可以用来解决约瑟夫环问题。
数组的元素是不能删的,只能覆盖。双链表 既可以向前查询也可以向后查询。
1、203移出链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。思路 :这道题一开始我以为简单,就是简单的链表遍历。但是我忽略了一个小细节,导致卡了一会,就是只有当下一个节点值不是要求移出的值时才步进指针,因为是要求值的时候我们断键重连后其实节点已经更新了,下一个节点应该再次被检查,不能步进指针 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ListNode* removeElements (ListNode* head, int val) { auto dumy = ListNode (0 ,head); auto *cur = &dumy; while (cur->next!=nullptr ){ if (cur->next->val == val){ cur->next = cur->next->next; }else { cur = cur->next; } } return dumy.next; }
2、 707设计链表
思路: 拿到这道题,一开始想的还是用单链表的遍历,这样每一个函数就都能写了。但是测试了运行13ms,击败42%的人,写的不是很好。估计得掌握双链表才能更快。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 class MyLinkedList { ListNode dumy; public : MyLinkedList () { } int get (int index) if (index<0 ){ return -1 ; } auto *cur = &dumy; int i = 0 ; while (cur->next!=nullptr ){ if (i++ == index){ return cur->next->val; } cur = cur->next; } return -1 ; } void addAtHead (int val) dumy.next = new ListNode (val,dumy.next); } void addAtTail (int val) auto *cur = &dumy; while (cur->next!=nullptr ){ cur = cur->next; } cur->next = new ListNode (val,nullptr ); } void addAtIndex (int index, int val) if (index<0 ){ return ; } auto *cur = &dumy; int i = 0 ; while (cur->next!=nullptr ){ if (i++ == index){ cur->next = new ListNode (val,cur->next); return ; } cur = cur->next; } if (i == index){ cur->next = new ListNode (val,cur->next); return ; } return ; } void deleteAtIndex (int index) if (index<0 ){ return ; } auto *cur = &dumy; int i = 0 ; while (cur->next!=nullptr ){ if (i++ == index){ auto temp = cur->next; cur->next = cur->next->next; delete temp; return ; } cur = cur->next; } return ; } };
3、206反转链表
代码随想录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { ListNode* temp; ListNode* cur = head; ListNode* pre = NULL ; while (cur) { temp = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } };
递归写法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public : void traverse (ListNode* head, ListNode *tail) if (head->next == nullptr ){ tail->next = head; return ; } traverse (head->next,tail); head->next->next = head; head->next = nullptr ; } ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { if (head == nullptr ){ return nullptr ; } ListNode tail = ListNode (); traverse (head,&tail); return tail.next; } };
代码随想录算法训练第三天|链表理论|203移出链表元素|707设计链表|206翻转链表